Holter
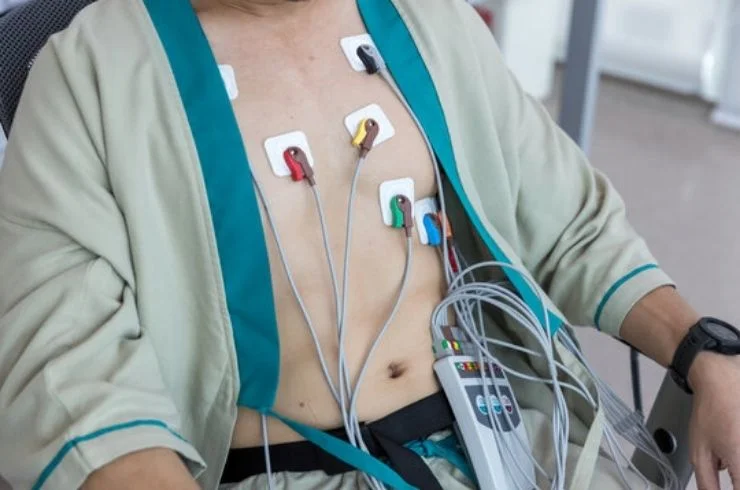
A Holter monitor is a portable device used to continuously record the electrical activity of the heart over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours, while the patient goes about their daily activities. This test helps diagnose irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) or assess heart function over time, particularly when symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or fainting occur intermittently and are not easily detected during a standard ECG.
During the procedure, small electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest and connected to the Holter monitor, which is worn on a belt or strap around the waist or shoulder. The device records the heart’s electrical activity, creating a continuous ECG tracing. Patients are usually asked to keep a diary of their activities and symptoms during the monitoring period to correlate with any changes in the heart’s rhythm.
Holter monitoring is particularly useful for:
- Detecting arrhythmias: Identifying irregular heart rhythms that may not appear during a routine ECG.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of heart medications.
- Assessing heart conditions: Like atrial fibrillation or other cardiac diseases.
- Monitoring symptoms: Like unexplained chest pain, dizziness, or fainting.
After the monitoring period, the recorded data is analyzed by a healthcare provider to detect any abnormal heart activity and determine the need for further testing or treatment. The Holter monitor is non-invasive, portable, and a valuable tool for diagnosing cardiac conditions that require continuous monitoring.

